College of Engineering Unit:
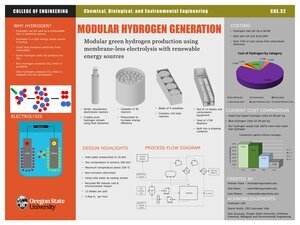
This project utilizes Hydrostar USA’s proprietary reactor and green electrolyte in the design of a hydrogen production system capable of running off renewable energy and being scaled utilizing its modular design. The reactors are similar to alkaline electrolyzes but differ in a few keyways. They can run off a proprietary, non-corrosive electrolyte that enables inexpensive reactor and process equipment materials. Additionally, they utilize fluid mechanics to separate the hydrogen and oxygen product streams rather than a membrane or other expensive technology, which decreases the cost of construction. The reactors are organized in the following modular design. 36 reactors run in a pressurized cassette, which is filled with B9 electrolyte. Four cassettes are in a blade and twelve blades are a pod. The pod is composed of a shipping container with the electrolysis system and a compression system. The compression system utilizes two compressors and heat exchangers in series to compress to hydrogen to 300 bar. The heat exchangers use the water feed stream to decrease operating costs and hydrogen temperature is kept below 300 oC to avoid hydrogen attack or autoignition. Given the modular design, pod composition can easily be modified to contain different numbers of reactors, allowing the system to fit more flexible design criteria.
Beyond the basic design functionality, an analysis of the systems costs was also conducted to determine system functionality. Each pod can create 2.9 kg of hydrogen per hour at $6.89 per kg. This is several times higher than the current industry standard of $1.8 per kg, which is manufactured using a highly polluting natural gas process. The primary cost driver is the energy needed for electrolysis, at 74.89%. Other costs include capital, 11.49%; compression, 4.54%; labor, 5.37%, and raw materials, 3.7%. The best way to decrease costs is improving the energy efficiency of the electrolysis process, which is currently being worked on by the Hydrostar team. The system can also be connected to renewable sources, like solar and wind, during peak production hours when energy costs are lower.
Industry Sponsor(s):
Project Communication Piece(s):
| Attachment | Size |
|---|---|
| 682.39 KB |