College of Engineering Unit:
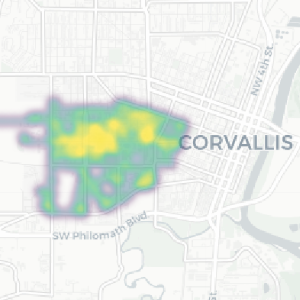
The purpose of this project was to use radiation detection equipment to create a heatmap of the background levels of ionizing radiation on the Oregon State University (OSU) campus. Using a highly efficient scintillation detector and GPS receiver, group members walked throughout the OSU campus and collected gamma ray spectra and location data. The data was saved in an easy to process format as a comma-separated values (CSV) file. After collection, the data was processed with Python to create a heatmap that shows the relative levels of background radiation detected by the scintillator. The heatmap covers the entirety of the outdoor areas of the campus, including pathways, roads, and parking lots. The collected spectra allowed for the determination of some of the prevalent radioactive isotopes on campus that contributed to the background radiation levels. The group also compared the efficiency of a lower cost (albeit smaller) scintillation detector to the higher cost one used to create the heatmap. The main goal of this project was to create a relatively simple method for logging background radiation data over a large area. Data gleaned from this project provides insight into the typical levels of background radiation in this specific location. Rapid collection and visualization of radiation levels over a large area is helpful for assessing environmental conditions and for comparing against after any changes in radiation levels (e.g., waste cleanup or emergency response). It is the hope of the group that this project encourages more research to be done into understanding background radiation levels in other locations.